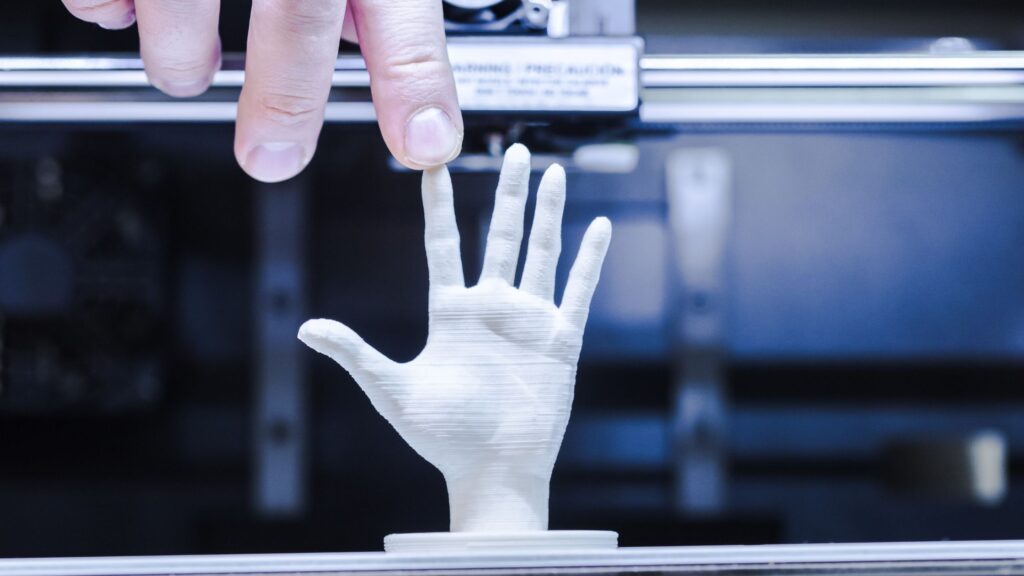
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a method of creating a three-dimensional object layer-by-layer using a computer-created design. It is a process of depositing multiple sequential layers of material over and over to create a project. The quality of the finished project depends on the type of material and technology used. The material chosen should satisfy the demand of the project.
How to choose the right material for the project? This is one of the most often asked questions in the 3D printing industry. There is no one answer to this problem as different products have different demands which require different materials to be used. A balance of both has to be achieved to make the designs functional and effective.
What are the properties to look for in a material:
- Melting temperature
- Elongation
- Impact strength
- Flexural strength
- Hardness
- Tensile strength
- Heat deflection temperature
There are 20+ materials available to choose from but we will discuss the best ones among them. The 3D Printing Guide given below will help you make the right choice.
1. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)

ABS has a long history in the printing industry. It is one of the very first 3D printing materials used for 3D printers. In fact, very well-known LEGO building blocks are also made from ABS.
It is a great material with low cost and has a higher glass transition temperature which means that it can withstand high temperatures without being deformed. It is mostly used in personal or household 3D printing and caters to other industries as well.
Advantages:
- Low Cost
- Available in a variety of colors.
- Has a longer lifespan
- Mechanically Strong
- Has good heat resistance properties
Disadvantages:
- The initial Setup is challenging
- Requires setup in a space with good ventilation
- Slight odor
- Parts tend to shrink leading to dimensional accuracy
Requirements:
- A heated bed is required with a temperature between 95-110 degree Celsius
- Kapton tape and ABS Slurry are required for build surface
- An extruder with a temperature between 220-250 degrees Celsius is required
- The cooling fan is not required
- Standard FDM printer and heated enclosure are recommended
2. Flexible filaments

Flexible filaments are made up of TPE or TPU and are known for their elasticity allowing the material to easily stretch and bend.
This material is used to produce highly elastic products. TPE has high impact resistance and is an excellent vibration dampener. It is available in a wide range of hardnesses.
Advantages:
- Flexible and soft
- Excellent vibration dampening
- Long shelf life
- Good impact resistance
- Fatigue resistant
- The head bed is not required
Disadvantages:
- Difficult to print
- Poor bridging characteristics
- Possibility of blobs and stringing
- May not work well on Bowden extruders
Requirements:
- Bed requires a temperature between 45-60 °C. A heated Bed is optional and an enclosure is not required.
- PEI and Painter’s Tape are required for build surface
- Direct Drive Extruder is Recommended with a temperature between 225-245 degrees Celsius.
- Part Cooling Fan is Required
3. PLA

Polylactic Acid is one of the most common 3D printing materials for FDM printers. It prints at a low temperature and is also biodegradable. It is inexpensive and also does not require a heated bed.
A variety of applications can be easily printed with this material. Being derived from crops, it is renewable and environmentally friendly.
Advantages:
- Low Cost
- Stiff and good strength
- Biodegradable and environment-friendly
- Does not require a heated bed
- Good dimensional accuracy
- Good shelf life
- Prints on cold surfaces
Disadvantages:
- Low heat resistance
- Can ooze and may need cooling fans
- The filament can get brittle and break
- Not suitable for the outdoors (sunlight exposure)
Requirements:
- Temperature between 45-60 °Cis required for bed
- Painter’s tape, PEI, Glass plate, and Glue stick are required to Build Surface
- The extruder should have a temperature between 190-220 °C
- Part Cooling Fan Required at 100% Fan Speed
4. Nylon

Nylon (known as polyamide) is a synthetic thermoplastic linear polyamide that is suitable to use when creating complex and delicate geometries.
It is primarily used as filaments in FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) or FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication) 3D printers. This material is inexpensive and recognized as one of the toughest plastic materials.
Advantages:
- Tough and partially flexible
- High impact resistance
- No unpleasant odor while printing
- Good abrasion resistance
- Corrosion resistance
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for moist and humid environment
- The low friction coefficient makes it difficult to stick to the build plate
- Shelf life of 12 months.
- Shrinks during cooling making prints less precise
Requirement:
- Bed Temperature between 70-90 °C is required
- Heated Bed and Enclosure is required
- Glue Stick and PEI are required to build surface
- The extruder should have a temperature of 225-265 °C
- Part Cooling Fan Not Required
5. Polypropylene (pp)

Polypropylene is a semi-rigid and lightweight material that is a valuable option for food containers and packaging appliances.
The semi-crystalline structure of the material causes the 3D printed parts to heavily warp upon cooling, making it challenging to 3D print. Polypropylene is tough and has good fatigue resistance making it ideal for low-strength applications like living hinges, straps, leashes, etc.
Advantages:
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Tough and has a good fatigue resistance
- Smooth surface finish
Disadvantages:
- Tends to warp easily
- Does not stick well to the building plate
- Low strength
- Expensive
Requirements:
- Bed between temperature: 85-100 °C is required
- Heated Bed is Required
- Enclosure is Recommended
- Packing Tape and Polypropylene Sheet can be used as a build surface
- The extruder should have a temperature between 220-250 °C
- Part Cooling Fan Required
6. Polycarbonate

Polycarbonate is known for its strength and durability. It has very high heat and impact resistance making it an ideal choice for tough environments.
Advantages:
- Impact resistant
- High heat resistance
- Naturally transparent
- Bendable without breaking
Disadvantages:
- Requires very high print temperatures
- Prone to warping
- High tendency to ooze while printing
- Absorbs moisture from the air which can cause print defects
Requirement:
- Bed between temperatures of 80-120 °C required.
- Heated Bed Required
- Enclosure Required
- PEI, Glue sticks, and Commercial Adhesive can be used to build surface
- The extruder should have a temperature between 260-310 °C
- Part Cooling Fan Not Required
7. PET/PETG

Like Nylon, PET or Polyethylene terephthalate is also one of the frequently used plastics. This material is used in thermoforming processes. It can also be combined with other materials like glass fiber to create engineering resins.
In 3D printing, PETG is used. It is a modified version of PET where G stands for “glycol-modified”. As a result, a filament that is less brittle, clearer, and easier to use than PET is formed. This filament is applicable in FDM or FFF technologies.
Conclusion
With proper knowledge equipped and the right materials being used, industrial 3D printing can be done efficiently. As the 3D printing industry grows, more and more materials will be used for making prototypes and will be compatible with different 3D printers. As with any new processes and equipment, there is a steep learning curve and this increases as you move from plastic to metal 3D Printing.
If you want to enjoy the ease of 3D printing, you can just outsource to a reliable 3D printing service provider. Your company actually doesn’t need to do 3D design and printing, mechanical design and drafting, 3D design modeling services, and in-house as they all can be done professionally with quality and accuracy by a local 3d printing company.